Wrist inflammation is a common problem that can affect both active and sedentary people. It is often caused by overuse of the wrist, repeated movements, or after a trauma such as a fracture or a radius fracture. The condition involves the muscles and tendons in and around the wrist becoming inflamed, leading to pain, swelling and reduced mobility of the wrist.
Common Symptoms of Wrist Inflammation
Recognising symptoms and treating them in time is crucial to avoid worsening the condition. Common signs of wrist inflammation are:
-
Wrist pain, especially with strain and movement
-
A throbbing pain in the wrist that worsens during the day
-
Swollen wrist with possible redness and heat increase
-
Pressure tenderness over the inflamed area
- Stiffness and reduced mobility of the wrist
-
Wrist feeling weak or unstable during activity
Symptoms may also radiate to the thumb or forearm, and the pain often occurs when you put strain on your wrist, for example when lifting or doing something you are not used to.
Causes of wrist inflammation
Inflammation of the wrist is usually caused by:
-
Repeated movements or overexertion in work or exercise
- Sudden stress on the wrist such as an accident or fall
- Underlying conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist or mb De Quervain
- Incorrect ergonomics or poor working postures
- Previous injury or fracture of the wrist
Depending on the cause, the condition can be acute or long-lasting.
Treatment of Wrist Inflammation
Treatment aims to reduce pain, reduce localised inflammation and relieve the wrist so that healing can take place.
Self-treatment and aids:
-
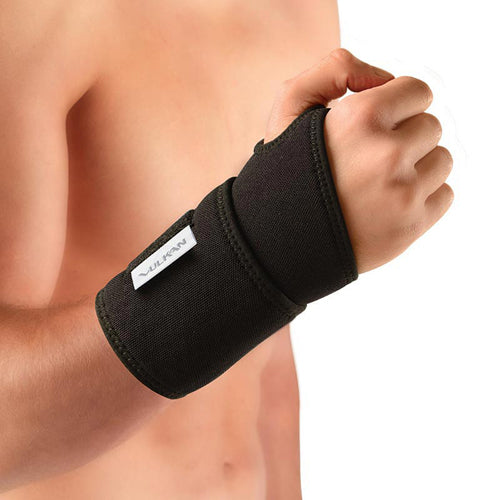
Wrist brace - an extra stable and supportive aid to stabilise the wrist and reduce strain.
- Splint for rest and immobilisation in case of severe inflammation.
-
Offloading the hand - avoid activities that put strain on the wrist or where pain is triggered.
- Use of related products such as ergonomic aids for work.
You can find wrist supports here at Sportsmart.
Professional treatment in healthcare:
-
A physiotherapist can help restore function, strengthen extensor tendons and reduce the risk of recurring problems.
-
MRI or ultrasound can be used to confirm the diagnosis and provide an accurate description of damage to tendons and tissues.
- In cases of severe inflammation, surgery may be required, especially if treatment has not been effective.
Prevention tips
To prevent the condition from recurring or worsening:
-
Reduce strain by adapting work environment and equipment
- Use stabilising and supportive wrist protectors during physical activity
- Avoid putting unnecessary or repetitive strain on the wrist
- Rest and recovery if you feel pain or wrist weakness
Wrist inflammation is often the result of repetitive strain, trauma or underlying disease. By recognising the symptoms of wrist inflammation early, and with the right treatment and relief, you can effectively relieve the symptoms. Use wrist supports, rest from strenuous activities, and seek help if pain persists or worsens - this will help you regain wrist function and avoid unnecessary pain.